How to Know if You Have Hiv
In the U.S., at that place's a skilful chance you could go a long fourth dimension without hearing anything nigh HIV. Many schools aren't required to teach sexual education—and of those that exercise, they're not required to teach accurate information. Every bit a result, whatsoever cognition yous have about HIV might exist solely from boob tube or Google, both of which can unfortunately lead to you believing incorrect, and even harmful, information.
The reality is that HIV is complex. Yes, it's a virus that can crusade biological illness, but it too has social and cultural origins—as well as social and cultural impacts. When people talk about HIV, information technology's hard to talk about any 1 of these aspects without bringing upwards all of them. Here'southward a primer on all these dissimilar aspects of HIV and how they all fit together.
OK, What Exactly Is HIV?
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. HIV has only 1 job: to brand more than HIV. When it enters a person's bloodstream, HIV hunts down a person's allowed cells (called "T cells" or "CD4 cells") and injects its own genetic code into them. It hijacks these cells, first turning them into factories that make more copies of the virus, and then eventually killing those cells.
While these HIV-hijacked immune cells are busy making more copies of the virus, they can't do their primary chore, which is defending your trunk from other viruses, bacteria, and infections that can cause illness—and that a fully functioning immune system tin usually beat on its own. That's why, in the early days of the epidemic, and so many people with HIV succumbed to illnesses: Their immune systems were weakened past HIV until they could no longer fight off other illnesses.
How Practice Y'all Go HIV?
In social club for HIV to go from ane person to another, two things demand to come into contact with each other:
- a bodily fluid that contains live HIV
- direct access to a person's bloodstream (sometimes called a "port of entry")
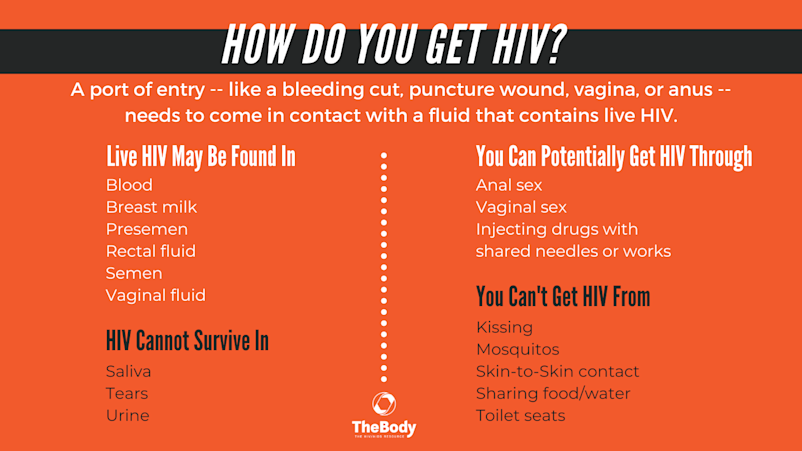
Common entry points into a person's bloodstream include:
- an unusual opening in the skin, like a cut or a puncture wound
- a mucous membrane, similar the vagina or anus
These body fluids potentially incorporate infectious amounts of HIV:
- Blood
- Breast milk
- Presemen (a.k.a. precum)
- Rectal fluid
- Semen
- Vaginal fluid
This ways you tin can potentially become HIV through:
- Anal sexual practice (bottoming may exist more of a adventure than topping)
- Injecting drugs with shared needles or other equipment used to share drugs, known as "works"
- Vaginal sexual activity
Infectious levels of HIV are not found in these fluids:
- Saliva
- Tears
- Urine
This means you cannot get HIV from:
- Kissing
- Mosquitoes
- Skin-to-skin contact, including a massage
- Sharing food or h2o
- Toilet seats
If someome living with HIV is on successful HIV handling, this reduces the virus in their bloodstream to such a depression level that they substantially can't transmit it to their sexual partners who are HIV negative.
What'southward the Departure Betwixt HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)?
People often use the terms HIV and AIDS interchangeably, simply they are two different things!
- HIV is the proper name of a virus. When you lot are diagnosed as HIV positive, it means that there are copies of the virus in your bloodstream, indicating that HIV has taken control of some of your immune cells.
- AIDS is the name of the syndrome a person develops subsequently HIV has so severely weakened their immune system that they're at take chances for developing illnesses a healthy allowed system would typically fight off.
- HIV is the simply crusade of AIDS.
- Information technology ordinarily takes many years of living with HIV and non taking HIV medications to develop AIDS.
In the early years of the HIV epidemic, most people living with HIV somewhen developed AIDS—and AIDS was often considered a death sentence. Today, once a person receives an AIDS diagnosis, they tin can take medication and go better, but because of how medical definitions piece of work, the official diagnosis of AIDS remains.
AIDS—which is short for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome—is a very specific medical definition. To be considered as having AIDS, one of these two things must be true:
- Your CD4 count is below 200 cells/mm3. CD4 cells are part of the body'due south immune system. They're a type of immune jail cell chosen a T cell, and they're responsible for fighting off infections in your bloodstream. A CD4 count is a exam that looks at the number of CD4 cells in your blood.
- You develop an "AIDS-defining status," also called an opportunistic infection. This is one of about two dozen specific illnesses (including several cancers and bacterial, fungal, or viral infections) that tin exist fatal for people with a weakened immune arrangement.
During the 1980s and 1990s, when HIV starting time became a huge health scare, AIDS was considered the final or stop stage of HIV infection. But that was during a time when effective HIV handling was all the same being adult. These days, HIV medications can—and oftentimes do—raise even some of the lowest CD4 counts back in a higher place 200, and can help the body restore the wellness of its immune system.
What Are the Symptoms of HIV?
In that location's no single, reliable sign or symptom of HIV infection. This is why the but trustworthy manner to know whether you have HIV is to get an HIV test.
The symptoms a person with HIV might experience depend on how long they've been living with the virus, and whether or not they're on handling. In that location are three major stages of HIV infection:
- acute infection (a.one thousand.a. primary infection)
- chronic infection
- avant-garde HIV disease (AIDS)
Astute Infection
Besides called chief infection, this phase typically occurs a few days to a few weeks after a person is exposed to HIV.
The most commom symptoms of acute HIV infection may be difficult to tell autonomously from the influenza, and might include whatever of the following:
- Fatigue (feeling tired or sapped of free energy)
- Fever
- Oral cavity sores
- Muscle aches
- Dark sweats
- Skin rashes
- Sore throat
- Swollen lymph nodes
If a person feels any symptoms from astute HIV infection, they usually go away by themselves within a few days or weeks—nearly the aforementioned corporeality of time it takes to get over a cold or the flu.
It's likewise of import to call up that plenty of people go through this acute stage of HIV exposure without feeling any symptoms at all.
Chronic Infection
This stage begins afterwards the acute infection menstruum ends. Chronic infection can final up to a decade or more if a person doesn't begin HIV treatment, and indefinitely if they are taking HIV medications.
A person may experience no symptoms during the chronic HIV infection phase. This is because HIV harms the immune system slowly, degrading information technology over a span of many years. If left untreated, the virus will continue to take over and destroy immune cells, turning them into HIV factories. When a person begins HIV handling, the medications end HIV from making copies of itself. This allows the immune organization to recover—or, if a person begins treatment early on enough after exposure, to avoid most of the harm HIV can crusade.
A person living with HIV who is on handling can remain in the chronic stage indefinitely. In fact, thanks to HIV medicactions, many people living with HIV now live a lifespan similar to people who are non living with HIV.
Avant-garde HIV Disease
When people living with HIV go a long fourth dimension without HIV treatment—normally 10 years or more—they'll usually enter the avant-garde infection phase, which tin be life-threatening. This is the stage when a person is diagnosed with AIDS.
Symptoms of avant-garde HIV disease vary widely, because HIV itself isn't usually what causes the symptoms. Instead, those symptoms are caused by another infection or disease that has taken root in the body because the immune system tin can no longer protect it.
During the worst years of the AIDS epidemic in the U.S. (in the 1980s and commencement one-half of the 1990s), people with advanced HIV disease experienced mutual symptoms and conditions such every bit:
- Kaposi'southward sarcoma, a blazon of cancer caused by a virus that can affect the pare, tummy, and lungs
- Meningitis, a swelling around the brain caused by viruses, leaner, or fungi
- Thrush (a.k.a. candidiasis), a fungal infection of the mouth and throat that makes it painful to swallow
- Wasting syndrome, in which people lose more than than 10% of their body weight
Dorsum in the 1980s and 1990s, AIDS was a very common and fatal syndrome. In that location were few treatments; the medications that existed involved taking up to 20 pills a twenty-four hours, and many had serious side effects. Today, a person living with HIV tin can exist on treatment that only involves taking one pill a day, with few (if any) side effects, that keeps their immune system healthy for decades.
Who Gets HIV?
Truth is, anyone tin can go HIV—a friend, a cousin, a colleague, or a partner. Regardless of a person's physical characteristics or identity, to transmit HIV, there only needs to be a fluid that contains HIV and access to a sexual partner's bloodstream.
In the U.S., HIV is all the same often thought of as a virus that generally affects gay people. While information technology's true that most new cases of HIV occur amidst gay men, HIV isn't a "gay disease." Instead, the virus tends to thrive wherever discrimination and poverty are at their highest—and where admission to safe housing and good health intendance is at its everyman.
In the U.S., the groups most heavily impacted by HIV are:
- Transgender women
- Gay men
- Black people
- Latinx people
- Other people of color, including Native American/indigenous people
- People living with disabilities
- People living in southeastern states
Racism and other inequalities put people of color, especially Black people living in the southeastern U.South., at a much higher-than-average adventure for HIV. While it's like shooting fish in a barrel to say that a person'south health is their ain responsibility, at that place are oftentimes many factors at play. In fact, a person's chance for various illnesses—including HIV—is based in part simply on whether they're built-in in an impoverished zip code.
Worldwide, if you desire to find the highest rates of HIV, expect in areas that are struggling to deal with legacies of colonialism, racism, and other societal instability. Some of the highest HIV rates in the world are amid people living in countries that were once colonized and are still underdeveloped, including much of Africa and South Asia.
Your race, sexuality, gender identity, state of origin, and any other personal identities or characteristics practise non somehow mean yous'll automatically get HIV. However, anyone with a marginalized identity may be at increased adventure for HIV infection because of the many unfair health intendance biases in our globe.

In the U.Due south., nearly all HIV infections in children under the age of 13 occur when the virus is passed to the kid when they are in their parent'due south womb or as they laissez passer through the birth canal, or through breastfeeding. However, prevention efforts combined with proper treatment—new antiretroviral medications given to the birthing parent before birth and the babe afterwards nascence, HIV diagnoses in infants continue to decrease.
Prior to these advances, approximately 25% of birthing parents in the U.S. living with HIV not on a therapeutic regimen passed the virus on to their babies. Nowadays, according to the Elizabeth Glaser Pediatric AIDS Foundation, of the approximately eight,500 HIV-positive pregnancies each year, at that place are less than 150 new babe HIV infections.
Teens and young adults, still, betwixt the ages of 13 and 24, especially among communities of color, represent 1 of the fastest growing HIV-positive groups in the U.S. In 2019, young people accounted for 21% (7,648) of all new HIV diagnoses. Yet, testing rates amid high school students remain low—according to recent information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), just 9% of U.S. loftier school students accept always been tested for HIV.
Older adults are another group disproportionately impacted by HIV. According to the CDC, more than half (51%) of the people with diagnosed HIV in the U.South.—and 1 in 6 people newly diagnosed—are 50 and older. Although older adults face up some of the aforementioned risks as other groups impacted past HIV, research shows that amid the factors that increase older people's risk for HIV are a reluctance to talk over sex with their healthcare providers, including testing for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections.
Similar to other groups, older people may also lack knowledge most HIV prevention and may be less likely to use prevention methods like condoms during sexual activity because they are less concerned nearly pregnancy. Certain age-related factors tin also put older people at a higher take a chance for HIV. For instance, vaginal dryness and thinning after menopause can atomic number 82 to tears in vaginal tissues during sex that may increment the risk of HIV manual.
It'southward important and even encouraging to mention another reason for the increase in older adults with HIV: Thanks to HIV medicines, they are living longer, healthier lives.
Where Did HIV Come From?
The short answer is: We're not certain how the HIV epidemic started.
The longer answer is: When it comes to where, when, and how HIV evolved into a virus that infected many millions of humans, we've learned a lot—but at that place'due south a lot more we take yet to learn. In the meantime, going back to the earliest days of the HIV epidemic, there'south been a lot of misinformation near how it all started. Many of those myths are still making the rounds today; all they do is worsen HIV stigma and create bigotry and discrimination against entire groups of people who don't deserve it.
Here'southward a few of the things nosotros know pretty confidently nearly the origins of HIV: HIV evolved from another virus, SIV, which is curt for simian immunodeficiency virus. SIV has existed in apes and monkeys for a very long time—potentially tens of thousands of years, if not longer. It appears to exist by and large harmless to these primates, at least in the form we meet today.
Humans can't get SIV—it's a primate-only virus. Only at some bespeak, a strain of SIV mutated to infect people, and HIV was born. Scientists believe this has happened more than than once, leading to at to the lowest degree two different strains of HIV, which nosotros call HIV-one and HIV-2. HIV-1 is past far the most common strain worldwide, while HIV-2 mostly appears in western Africa.
We don't know for certain when or where HIV fabricated the leap into humans, although some of the most common theories today—those that are nearly heavily backed by reputable scientific discipline—advise that information technology happened in Africa in the early on 20th century. We also don't know exactly how HIV starting time infected people, though there are plenty of unproven (and potentially harmful) ideas, including the hunting/butchering of monkeys or contaminated needles from vaccination campaigns.
Every viral epidemic starts somewhere. There are endless viruses in the world, and they're constantly evolving and mutating. Sometimes, those things happen in way that leads the virus to infect, and even kill, big numbers of people. HIV, information technology's turned out, has been i of those viruses. But that fact doesn't mean that the location where this epidemic happened to start deserves to be blamed for information technology—or that whatever of the people who accept been caught up in HIV's growth from a local outbreak to a decades-long global pandemic deserve special blame, either.
How Can I Prevent HIV?
If you are HIV negative and want to know how to stay negative, you have quite a few options.
The first affair you should know is that if you are having sexual practice with someone living with HIV who is on medication and has an undetectable viral load, there is no risk of you acquiring the virus. At that place are 2 normally used terms for this: "undetectable equals untransmittable" (or U=U for curt) and "treatment equally prevention."
In improver to that fact, people who are HIV negative besides have options under their command that can empower them to stay HIV negative. Since HIV needs access to the bloodstream and bodily fluids containing the virus in lodge for infection to occur, nigh methods of protection intermission downwards into iii categories:
- barrier protection
- biomedical prevention
- syringe exchange (or damage reduction)
Barrier Protection
Barrier protection puts a concrete barrier between a person and a fluid containing HIV. The most pop methods include insertive condoms and receptive condoms.
- Insertive condoms are worn by insertive partners—for instance, a person who puts their penis into another person'due south anus or vagina.
- Receptive partners can wear receptive condoms in their anus or vagina.
Biomedical Prevention
While barriers make sure people don't come into contact with fluid containing HIV, biomedical prevention stops HIV from gaining a foothold in a person'south body. There are two types of biomedical intervention: PrEP and PEP.
- PrEP, short for pre-exposure prophylaxis, is a plan that involves a person who is confirmed to be HIV negative taking a prescription medication to forbid exposure to HIV. Information technology tin be taken daily or in an "on-demand" schedule. At the moment, at that place are two different medications that have been approved in the U.South. for use as PrEP. Other types will be available in the future.
- PEP, short for post-exposure prophylaxis, is a month-long course of prescription HIV medications meant to foreclose infection. If you think you accept been exposed to HIV through sex, for case, yous tin can brainstorm PEP within 72 hours after the human action.
Syringe Exchange
If you lot inject drugs, several states in the U.S. take programs where you can exchange used needles and syringes for fresh ones to reduce the run a risk of HIV manual.
How Does HIV Testing Work?
The simply way to acquire for sure whether y'all're HIV positive or HIV negative is by getting an HIV exam. In about of the U.S., information technology's about as easy to go an HIV test as it is to get a pregnancy examination.
HIV testing is recommended as a routine part of health care for everyone in the U.S. between age 13 and historic period 64. More frequent testing (at least one time a year, if non more than) is recommended for people who are sexually active (regardless of whether it'south anal or vaginal sex, or whether yous're giving or receiving), especially if it's with multiple partners. Ditto for people who share injection drug equipment with anyone else.
At that place are 3 main types of HIV tests:
- At-habitation HIV tests. These are kits you can guild online or option up at a local pharmacy. Using a tiny sample of saliva or blood, they'll requite y'all a preliminary test result—if information technology'south positive, y'all'll desire to follow upwardly with a health intendance provider for a confirmatory test. The typical cost is around $thirty to $45.
- Rapid HIV tests. These are saliva or blood tests that a wellness intendance provider or other certified tester can give y'all. They provide a preliminary outcome in less than 20 minutes—and some tin can exist as quick as v minutes or less. If a rapid test is positive, your will need to get a full blood test to confirm the result.
- Confirmatory HIV tests. All HIV tests are accurate, but confirmatory tests do the best job at rooting out "false positives," which tin can happen rarely with at-home and rapid tests. The gold standard is called the "4th generation HIV test." A health care provider volition take a sample of your blood and send information technology to a lab for in-depth testing; results typically take a few days to come back, sometimes longer, simply will provide you with the most reliable result.
If yous were very recently exposed to HIV—as in, within the past couple of weeks—older HIV tests may not be able to spot your infection. That'due south because information technology takes several days for the virus to make its manner through your immune system and begin to create new copies of itself—and weeks or months for your torso to begin developing its ain antibodies to fight off the HIV. (Some HIV tests piece of work by detecting the virus itself, while others work by detecting the HIV antibodies your torso creates.)
If yous're concerned that a specific result happened to put y'all at gamble for HIV, experts recommend that yous:
- Talk to a health intendance provider immediately—within 72 hours, if possible!—almost the possibility of starting PEP, or post-exposure prophylaxis. PEP can prevent an HIV exposure from becoming an infection.
- Wait to get tested for HIV until it'southward been more than two weeks since the risky event.
- Talk to a health care provider about whether an HIV prevention prescription—too known as PrEP, or pre-exposure prophylaxis—might exist right for you.
Is At that place a Cure for HIV?
No, in that location is no cure. But cheers to scientific discipline, people who are living with HIV oftentimes alive long, salubrious lives.
There is an extremely small number of cases where a person with HIV was cured of their infection with a type of os marrow transplant. Merely these cases haven't been replicated on a large scale: The procedures are extremely hard to exercise, and they're potentially deadly.
Meanwhile, researchers across the world are exploring a number of different potential means to cure HIV more safely and reliably. But nosotros're probably still many years away from having a cure.
Many HIV activists likewise feel that, even if there is a cure, at that place may be unequal admission to it—equally there currently is with the cure for hepatitis C.
Volition HIV Affect How I Alive My Daily Life?
Living with HIV can have serious consequences for your trunk, simply those physical effects tin be prevented or treated by taking medication prescribed by a health intendance professional. That takes care of your body—but what about your mental health and well-being?
While the medical community has worked difficult to make HIV a manageable, chronic illness, our gild still has a long way to go in eradicating HIV stigma and making the lives of people living with HIV easier.
HIV stigma is a term that refers to the negative and unfounded ideas near HIV that people have due to myths, misinformation, and outdated attitudes associated with the illness. Here are some examples of stigma:
- Treating someone with HIV differently than you would treat someone who is HIV negative.
- Using the discussion "clean" to denote being HIV negative.
- Assertive all gay people have HIV.
- Believing that having HIV makes y'all less worthy or desirable than another person.
When a person adopts these ideas, they can in plough create shame and fright for people living with HIV, or what nosotros might telephone call internalized HIV stigma. HIV stigma can have terrible consequences. It can deter people from getting tested in the first place. It can lead people to avoid health care or to receive worse wellness care than they deserve, resulting in poorer concrete and mental wellness. People with HIV also face up disproportionate levels of intimate partner violence because of their status.
When a person acts out their stigma against someone living with HIV, it tin can atomic number 82 to discrimination. In the U.S., at that place are laws relating to HIV—some that assist with discrimination, but some that hurt.
Helpful: HIV is a protected health status, and an employer cannot fire someone for living with HIV.
Hurtful: As of 2018, 26 states accept laws that make HIV exposure a crime. While in that location accept been legislative victories in some states, including Iowa and Colorado, the reality is that many states withal prosecute people with HIV, fifty-fifty in cases where there was no HIV transmission.
Across these problems, people living with HIV have a lot to manage in order to stay good for you and happy. Only with a clear plan, access to adept health care, successful HIV treatment, and a potent support network, the virus tin go just another fact of life—a life that doesn't have to be one day shorter because of their HIV condition.
This video on how much of a concern HIV is in the U.Due south. today, featuring David Malebranche, Thou.D., is part of the #AskTheHIVDoc series past Greater Than AIDS, a public outreach program run past the Kaiser Family Foundation.
- Medical Definition of AIDS: AIDSinfo. (n.d.). "HIV/AIDS Glossary: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)." clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/en/glossary/caused-immunodeficiency-syndrome-aids
- AIDS-Defining Weather condition: U.S. Department of Veterans Diplomacy. (n.d.). "AIDS-defining illnesses." hiv.va.gov/patient/diagnosis/OI-AIDS-defining-illnesses.asp
- Stages of HIV: AIDSinfo. (2019). "The Stages of HIV Infection." hivinfo.nih.gov/understanding-hiv/fact-sheets/stages-hiv-infection
- HIV Symptoms: HIV.gov. (2019). "Symptoms of HIV." hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/symptoms-of-hiv
- HIV Origins -- Some Electric current Theories: Nature Inquiry. (2018). "Origin story." nature.com/manufactures/d42859-018-00008-6
- HIV Origins -- Myths and Assumptions: American Journal of Public Health. (2015). "Rumors and Realities: Making Sense of HIV/AIDS Conspiracy Narratives and Contemporary Legends." ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/x.2105/AJPH.2014.302284
- HIV Testing: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). "HIV: Testing." cdc.gov/hiv/basics/testing.html
- HIV Test Types: U.Due south. Food and Drug Administration. (2019). "Complete List of Donor Screening Assays for Infectious Agents and HIV Diagnostic Assays." fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/complete-list-donor-screening-assays-infectious-agents-and-hiv-diagnostic-assays
- Who Gets HIV: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2018). "HIV Surveillance Written report, 2017." cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveillance-written report-2017-vol-29.pdf
- HIV Stigma: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). "Facts Almost HIV Stigma." cdc.gov/hiv/nuts/hiv-stigma/alphabetize.html
glassoprobbild1991.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.thebody.com/health/hiv-aids